I. How to Set Up an Office in Vietnam
Read through this guide to setting up a business in Vietnam. From company registration to setting up an office and hiring employees.
Before setting up an office in Vietnam, you must understand local regulations and market dynamics. This article will cover everything you need to start an office in Vietnam. This includes the types of legal entities, requirements, and registration process. We will also talk about key locations to start an office in Vietnam, and the employee hiring process.
II. Legal Framework for Company Registration Process in Vietnam
1. Registering a legal entity in Vietnam
To set up your office in Vietnam, you must register a legal entity there. There are several types of companies you can start. One of the most common types is a Limited Liability Company (LLC). Depending on the industry, an LLC can allow up to 100% foreign ownership, notably in IT, trading, manufacturing, short-term training centers, and language schools.
There are two types of LLCs you can establish in Vietnam:
1. Single-Member LLC – only one member has exclusive rights over decision-making and holds full responsibility for the company’s liabilities.
2. Multi-member LLC – can have between 2 to 50 members who share responsibilities depending on their capital contributions. A Member’s Council typically governs these companies with a director managing daily operations.
If your main objective is to establish an extension of your company, you can set up a branch office in Vietnam. A representative office can also act as an extension to your business but is not permitted to generate income and acts only as a liaison office.
2. IRC and ERC Requirements in Vietnam
Before an office in Vietnam is fully operational, you need to register your business with the Department of Planning and Investment (DPI). Foreign entities are required to obtain an Investment Registration Certificate (IRC) under the Law on Investment (2020). Afterwards, you can obtain an Enterprise Registration Certification (ERC) to legally operate in Vietnam. Here’s what you will need:
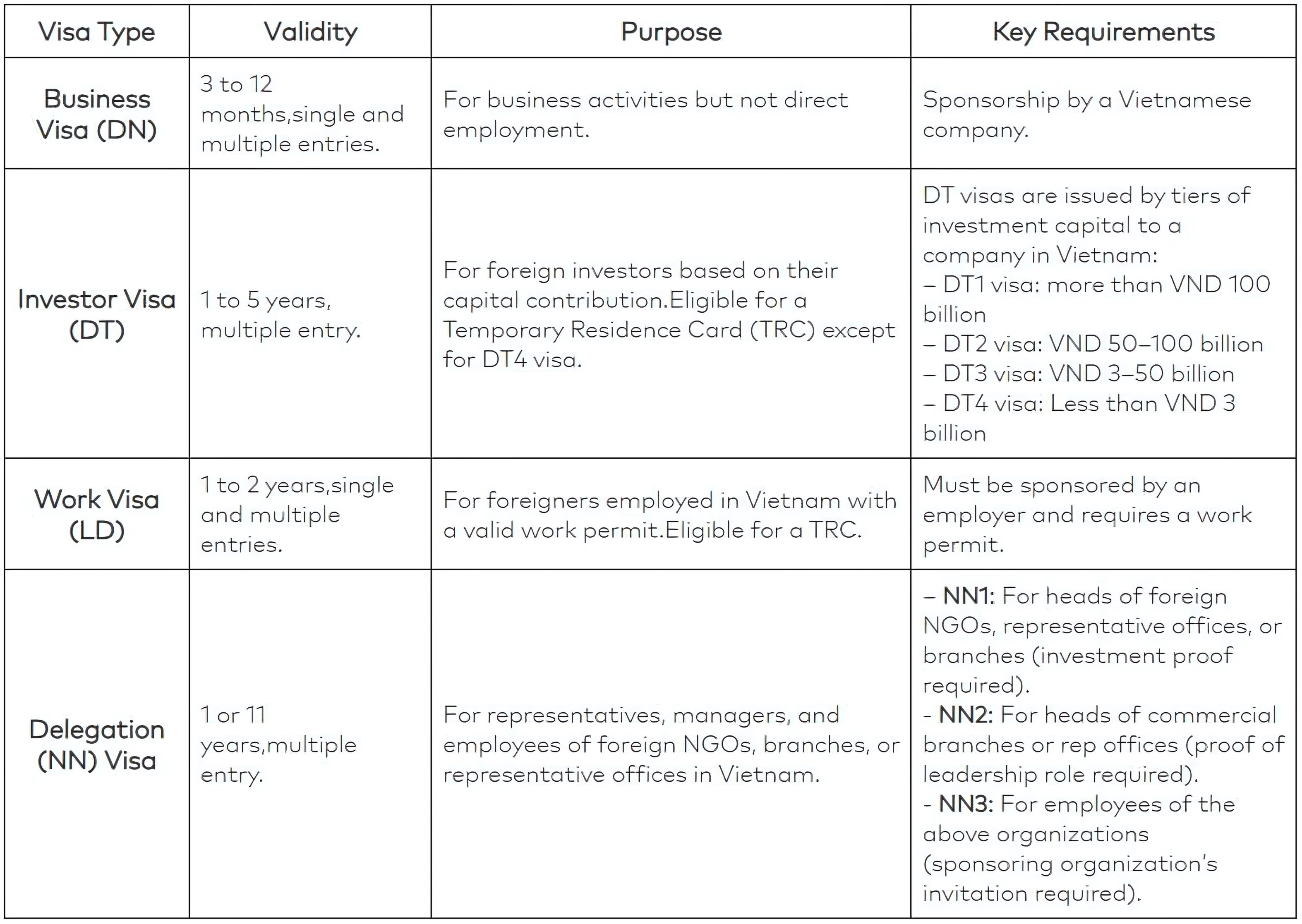
3. Post-registration Compliance
Once you have obtained both the IRC and ERC, you can then undertake the following mandatory steps for your company in Vietnam to complete your office setup:
• Register with the local tax office – Upon receiving the ERC, you must register your company with the General Department of Taxation. This is mandatory for all businesses earning income in Vietnam. The local tax office will issue a company registration code that also serves as a tax code number.
• Open a bank account for business transactions – you will also need to open a corporate bank account in Vietnam which will be used for all business transactions.
• A public announcement about your registration – after registration, companies must make a public announcement regarding their registration on the National Enterprise Registration Portal within 30 days of receiving their ERC.
III. Other Considerations for Starting an Office in Vietnam
1. Key Locations for Setting Up an Office in Vietnam
An important aspect of starting an office in Vietnam is deciding where it’s going to be located. Luckily, Vietnam has plenty of locations to start an office, each with unique advantages to choose from based on your specific business model and objectives. Here are popular locations to start a company in Vietnam:
• Ho Chi Minh City (HCMC) – as the largest city in Vietnam, HCMC is the country’s economic powerhouse. HCMC is home to numerous corporate headquarters with a large expatriate community. Ho Chi Minh has diverse economic activities including finance, manufacturing, tourism, and technology.
• Hanoi – the capital city and political center of Vietnam, Hanoi is known for its rich history and cultural significance. It is a major hub for e-business and technology with a focus on high-tech industries. It is also close to important trading routes and neighboring countries.
2. Average Cost of Starting a Company in Vietnam
Although there are no minimum requirements for most sectors, the Department of Planning and Investments recommends roughly around ~ USD 10,000 to cover initial expenses. Certain sectors, however, have specific capital requirements due to regulatory standards:
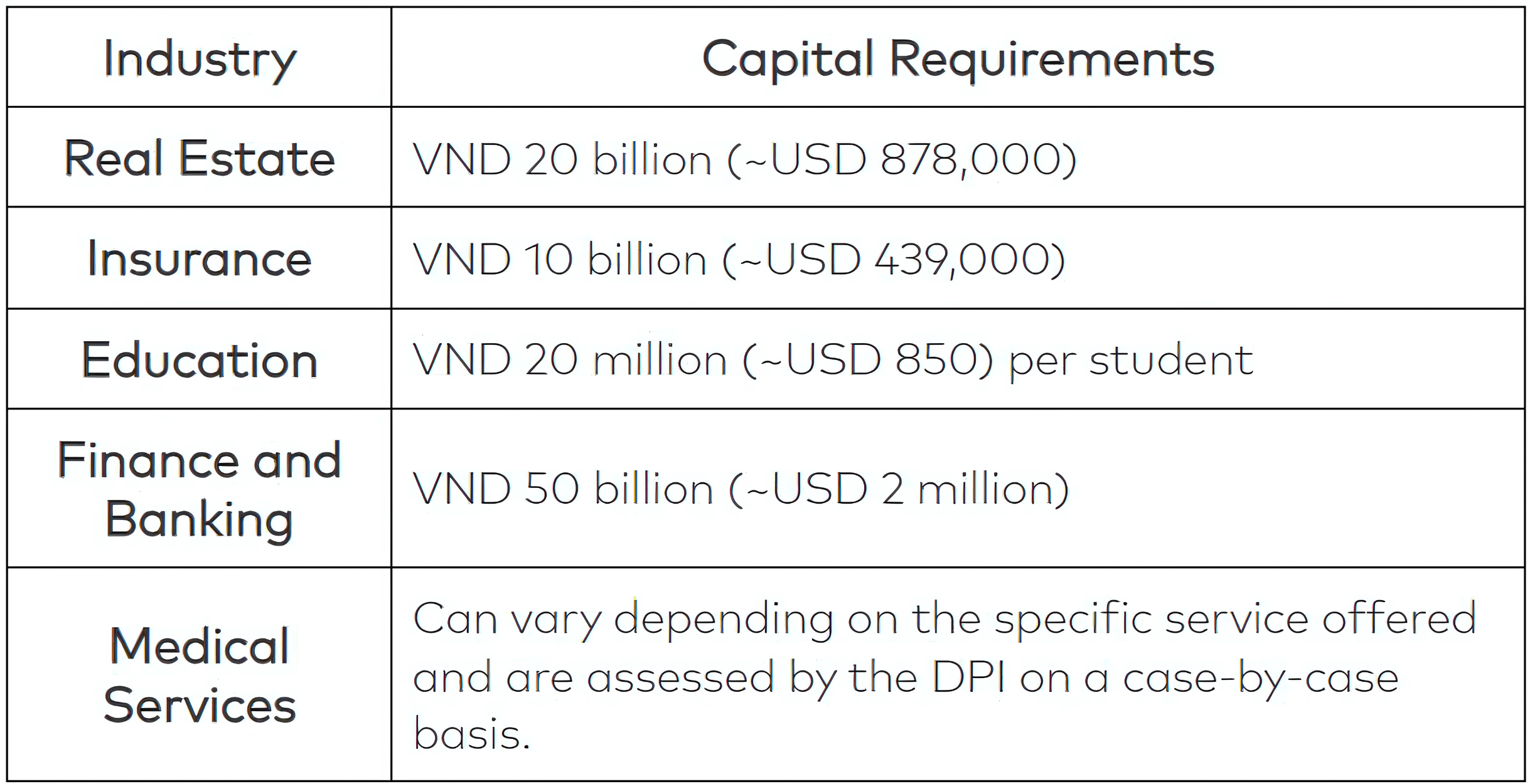
Apart from the capital requirements, you also need to consider office space rental costs. This may vary depending on the region and how much space you will need for your office in Vietnam, as well as the location. The Ministry of Construction in Vietnam rates buildings into three tiers depending on the architecture, infrastructure, and management services of the building. Different regions have different costs for each tier. Here’s how much office space would cost in HCMC and Hanoi:
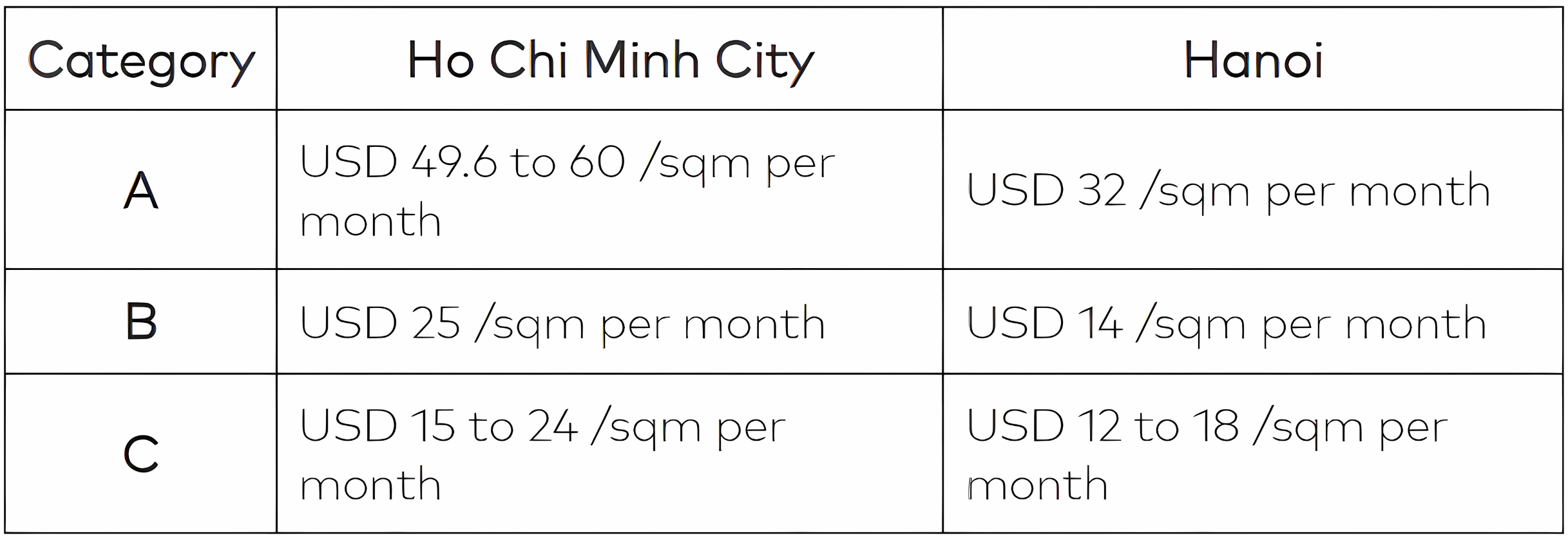
3. Hiring Employees in Vietnam
To hire employees in Vietnam, your company must adhere to the country’s Labor Code. This outlines the maximum working hours (maximum of 48), overtime pay (150% to 200% of regular wages), and employee rights to unionize. The Labor Code allows for probation periods of up to two months for managerial positions and one month for other roles.
As a business owner, you are also required to contribute to your employees’ social insurance. This includes health insurance, unemployment insurance, and pension contributions. The total contribution rate is approximately 32% of the employee’s salary (with the employer covering around 21%).
Foreign workers are required to obtain work permitt before commencing employment in Vietnam. To qualify, you must do the following:
• Demonstrate that no qualified Vietnamese candidate is available for the position.
• Submit an application that includes proof of recruitment efforts.


